Skeletal system
Hydrostatic skeleton:
Skeleton that is common among worms and jelly fish.
The coelom is filled with fluid which makes the animal rigidSimilar to a water ballon
This can help the animal move by squeezing muscles around the fluid
Exoskeleton:
Skeleton that is common among insects and mollusks
Skeleton present on the outside of the body
The skeleton is usually made of a nitrogenous carbohydrate called chitin
Endoskeleton:

Skeleton common in mammals
Skeleton is present on the inside of the body
They allow animals to grow larger by supporting more mass and doesn't require molting
Human adults have around 206 bones and 32 teeth
The place where bones connect to each other via ligamentsFibrous band of collective tissue joining bones to each other is called a joint
There are:
- 3 bones in each ear,
- 1 horseshoe shaped boneHyoid bone, only bone to not be connected to other bones,
- 5 in each arm,
- 26 bones in each foot,
- 4 in each leg,
- 8 skull plates,
- 14 face bones,
- 24 ribs,
- 1 sternum,
- 26 in the spinal column,
- 2 hip bones
Cartilage:
Smooth connective tissue that is more resilient than muscle but less than bone
It is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane
It is made of cells called chondrocyte
Formation of new bones:
Is is also called ossification
New bone starts off as cartilage and the chondrocytes start dividing and secrete collagenA fiber protein and other proteins to form a framework for bones to form on
Blood vessels in the cartilage bring cells called osteoblasts
The osteoblasts secrete a gelatinous substance that is a combination of collagen and a polysaccharide, this acts like glue
They then start absorbing minerals and salts from the blood, especially calcium and phosphate and depositing them onto the matrixMaterial between a eukaryote's cells
The calcium and phosphate form calcium phosphate with the help of enzymes secreted by osteoblasts
Calcium phosphate crystallizes to form the bone matrix, around ⅓ of the bone matrix is calcium phosphate and the other ⅔ is proteins
Even the mineralized part of the bone is living tissue filled with blood vessels
Structure of the bone:
The bone matrix forms in 2 layers
The outer layer is called the cortical bone or the compact bone
The compact bone is hard and dense and makes up 80% of the mass of the bone
The inner layer is called the Trabecular bone or the spongy bone
The spongy bone is softer and more porous, it contains the bone marrow and the fatty tissues in larger bones
The bone marrow produces blood cells in a process called hematopoiesis, they produce around 500 billion blood cells every day
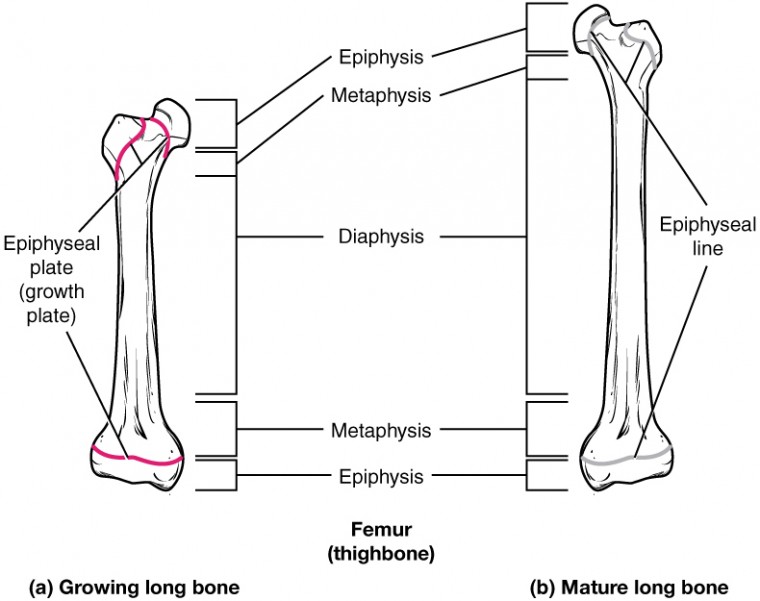
The larger bones have similar structure to each other
The middle part is called the diaphysis, each rounded end is called an epiphysis and between the diaphysis and epiphysis is the metaphysis
In growing kids, a new tissue form in a part of the metaphysis called the epiphyseal plate
Bone production occurs in the epiphyseal plate and stops at around 25 years of age
At 25, your epiphyseal plates harden
Bone lengthening is stimulated by growth hormones secreted from various glands but mainly from the pituitary gland
Pituitary gland is the size of a kidney bean and is situated at the base of the brain
Bone remodelling:
Every year as an adult, around 10% of the skeleton is remade
Osteoclasts are cells that breakdown bone
At the start of remodelling, osteoclasts are sent due to hormone signals through the capillaries to the site of microscopic fractures
Osteoclasts secrete an hydrogen ions which dissolve the calcium phosphate, collagenaseEnzyme which breaks collagen, Cathepsin K which catalyses collagenase and some hydrolytic enzymeEnzymes that breakdown larger molecules using water
The calcium phosphate is broken into calcium ions and phosphate ions and carried to the capillaries
This process of absorption of tissue into circulatory is called resorption
After the osteoclasts finish, they send a hormone signal to the osteoblasts to start remaking the bone
This is regulated by hormones that maintain the levels of calcium in blood
The glands involved are the parathyroid gland and the thyroid
Parathyroid gland triggers osteoclasts when calcium in blood plasma is low
Thyroid gland triggers osteoblasts when calcium in blood plasma is high
Thyroid gland regulates calcium reabsorption in kidneys and the amount of vitamin D
Vitamin D helps absorb calcium in the small intestine




